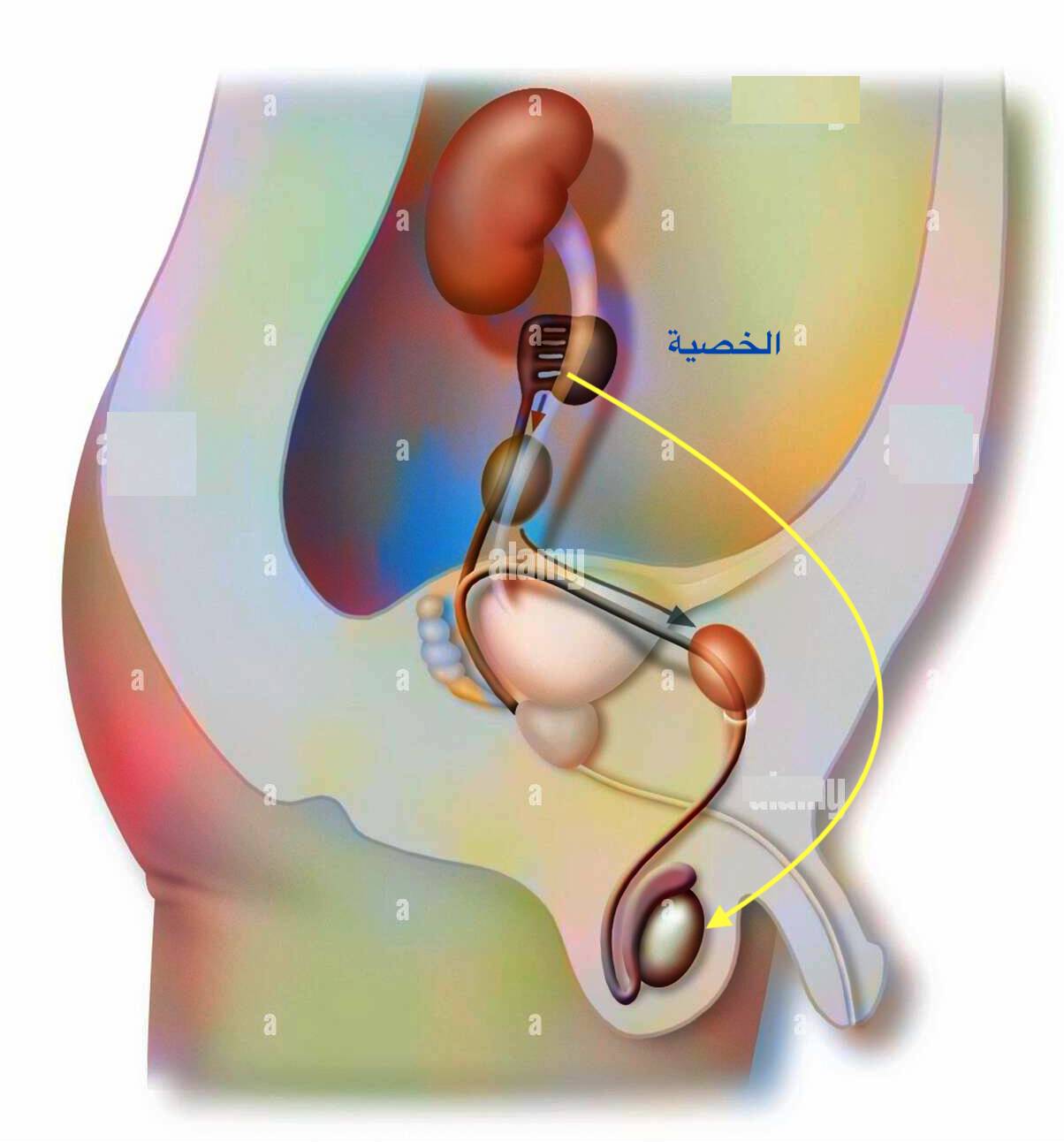
Undescended testicle
At least there is one male child between every 100 live births will have one or both of his testicle not in the proper position at the bottom of his scrotum.
Normally the scrotum of the full-term baby is divided into 2 compartments; each have a testicle, which was formed and developed high in the abdomen at a site near the kidney, but it starts to descend down from the 3rd month of the intrauterine life.
One of the major differences between boys and girls is to have the gonads (the factory for formation of ovum and sperms) outside the body in the scrotum.
Ovary which is the counter organ to the testicles lies high in the abdomen of the girl, but man should have the factory for formation of sperms outside the body and at 2oC lower than the rest of the body.
Causes of Undescended Testicle:
- Prematurity: Premature babies had a higher incidence; but many of them may improve spontaneously.
- Congenital: Many cases had a family history of the same disease affected the father or one of siblings
- Hormonal: Testosterone and other less important hormones may play a role in the incidence.
- Mechanical factors: many cases may have a hernia or other sorts of adhesions that obstacle the testis from normal descend.
- There are many general diseases and syndromes had a higher incidence.
Hazards: Why the undescended testicle should be operated to bring it down to the bottom of the scrotum and to fix it there?
- It had been proved with many animal experiments and statistical studies that the undescended testicle if left high without surgery, it will lose its capacity to produce sperms or it may produce abnormal sperms, (Non treated undescended testicles are responsible for many cases of infertility)
- Testicle should be fixed in the scrotum before the first birthday of the boy; it will lose from 20 to 40% of its capacity if it is left untreated for 2 years.
- At least 60% of the capacity of the undescended testicle will be lost at the 6th
- Undescended testicle will lose completely its capacity to produce sperms at puberty.
- The undescended testicle will be more liable for trauma and torsion.
- There are several studies proved that the undescended testicle may be liable to develop malignancy later on, especially the testicles which lie higher in the abdomen and left for longer time without management.
- One important point for me is the psychic trauma for the child, if the family ignored his problem till older ages.
Management:
- Undescended testicle should be diagnosed early and to be differentiated from the normally retractile testicles, which is a normal physiological condition in which the testicle is more mobile and moving up to the inguinal canal and down to the scrotum easily and frequently.
- Babies diagnosed before 6 months of their age can wait for a couple of months.
- It is better to fix the testicle before the age of one year.
- Surgery can be done classically through a small incision or through the laparoscope.
- The operation should be done under general anesthesia, which is so safe nowadays.
- Usually, the child can resume feeding two hours after surgery and can go home after 4-6 hours.
- Older children can go the kind garden next week after surgery.
- The role of hormones for treating the undescended testicle is doubtful.
-
For Arabic, please click here.